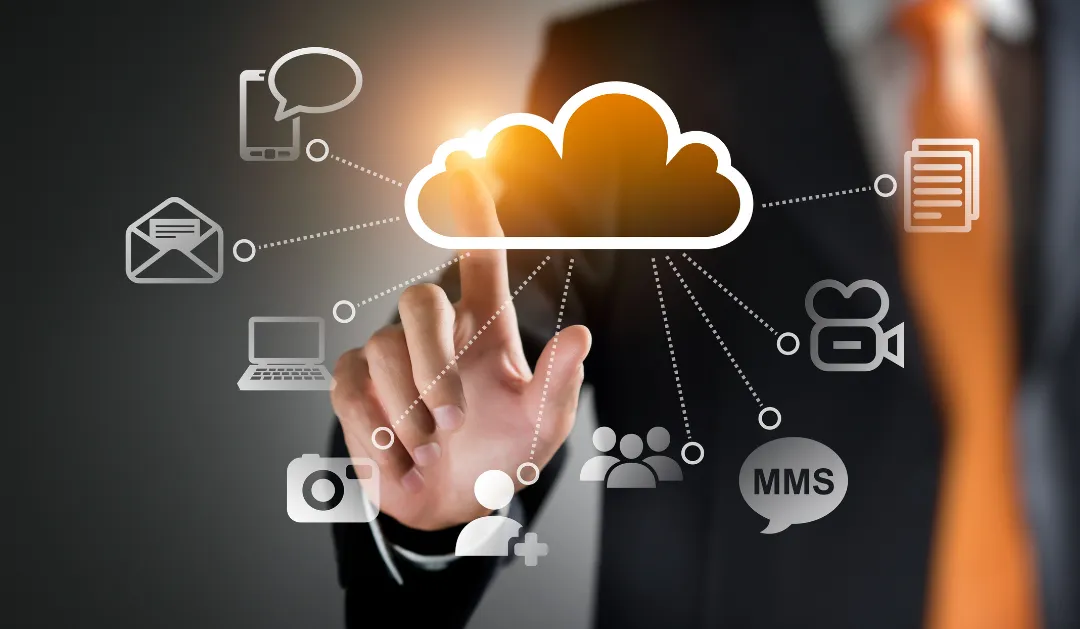
Even if you aren’t aware of it, you are most likely using cloud computing right now. If you use an online service to edit documents, watch movies, listen to music, send email or store pictures and other files, cloud computing is most likely behind the scenes.
Data storage has become a priority in every field. As the number of computer and mobile users has increased,so has the demand for data storage. Large and small-scale organisations nowadays rely on data, and often spend a lot of money to maintain this data. Cloud computing is the solution for such data storage. Let’s find out what this technology is all about-Basics of Cloud Computing.
Introduction To Cloud Computing
The term “cloud computing” refers to the storage and access of data and computer services through the internet. It does not save any information on your computer. Rather, it is a general term that refers to the on-demand availability of computer services such as servers, data storage, networking, databases, etc. on demand.
The word “Cloud” originated from a network design that the network engineers used to depict the location of various network devices and their interconnection.
The primary goal of cloud computing is to provide access to data centers to many users. Users can also gain access to data stored on a remote server.
How Cloud Computing Works?
Cloud computing functions by allowing the client/user devices to access data from remote servers, databases, and computers through the internet.
An internet connection links the front end (accessing client device, browser, network, and cloud software applications) to the back end (databases, servers, and computers).The back end acts as a repository for storing data that can be accessed by the front end.
A central server manages the communication between the front and back ends. The central server relies on protocols to allow data sharing. For handling communication between multiple client devices and cloud servers, the central server employs both software and middleware.
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Not all clouds are the same, and not every type of cloud computing is appropriate in every case. A variety of models, kinds, and services have emerged to offer the best solution for the needs of the user. There are three methods to utilize the cloud services: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.

1. Public Cloud
Public cloud services are owned and managed by third-party cloud service providers, which deliver their computing resources such as servers and storage via the Internet.
The cloud provider owns and manages the hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure in a public cloud. The user can access these services and manage their account with the help of a web browser.
Amazon, Google, Microsoft, IBM, Oracle, and others offer public cloud services. Hundreds or thousands of individuals share the resources. Gmail and Google Drive are examples of Public Cloud Services.
2. Private Cloud
A private cloud refers to cloud computing services that are only used by one company or organisation. A private cloud can be physically located on the company’s data center. Some organizations also use third-party service providers to host their own private clouds. A private cloud is one that keeps its services and infrastructure maintained on a private network.
Private clouds guarantee a high level of protection and privacy to data through firewalls and internal hosting. It also ensures that third-party providers do not have access to operational or sensitive data.
Examples of private cloud are HP Data Centers, Microsoft, Elastra-private cloud, and Ubuntu.
3. Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud is a combination of both public and private clouds. Companies and organizations choose it for the sake of data protection and security. Because it is economical, the demand for this sort of cloud service is increasing.A hybrid cloud provides better flexibility, security, and compliance by allowing data and applications to flow between private and public clouds.
An e-commerce store is one of the hybrid cloud examples. A sudden increase in demand for products makes it difficult to store information and data in a secure location, which is why hybrid cloud services are in high demand to keep data safe and secure while also making space available for the smooth operation of resources.
Examples of Cloud Computing Services

Cloud computing examples include the following:
Google Docs and Microsoft Office 365: Users may use the internet to access Google Docs and Microsoft Office 365. They can be more productive with these resources since they can access business presentations and spreadsheets saved on the cloud from any device at any time.
Email, Calendar, Skype, and WhatsApp: Emails, Google Calendars, Skype, and WhatsApp utilize the ability of cloud to provide users remote data access, allowing them to access their personal data on any device, whenever and wherever they wish to.
Zoom: Zoom is a cloud-based audio and video calling platform that records meetings and saves them to the cloud, allowing users to view them at any time.
Benefits of Cloud Computing

Omnipresence: The cloud is everywhere, and you can’t get away from it. Its ubiquity allows easy access to functionality, traceable data, and transparency. It allows several people to work on the same project without any difficulties. This,in turn,not only saves costs but also helps to establish a strong work model.
Data Security: Data security is probably one of the most significant issues that keep business owners awake at night. Cloud computing can assist to ease some of this anxiety. Though some people may claim that its open platform and ease of access makes it an easy way for hackers, it’s actually the opposite. Databases and files are heavily encrypted. They are transferable without the chance of being hacked.
Cost-Savings: Once you’re on the cloud, having quick access to company’s data will save you time and money when starting new projects. And, for those people who are concerned about paying for features they don’t need or desire, most cloud-computing services are ‘pay as you go’. This implies that if you don’t take use of what the cloud has to offer, you won’t have to spend money on it.
Mobility: Because information is stored in the cloud server, users may access it from anywhere using any device with an internet connection.This eliminates the need to carry about USB devices, external hard drives, or several CDs to access data. Corporate workers may access data via smartphones and other mobile devices, allowing remote employees to keep in touch with coworkers and customers.
Data Recovery: Data recovery is a concern for all organizations. Storage of data on the cloud ensures that users can always access their data, even if their devices,such as laptops or smartphones,are inaccessible. Organizations can easily restore their data using cloud-based services in the case of an emergency,such as a natural disaster or a power shutdown.
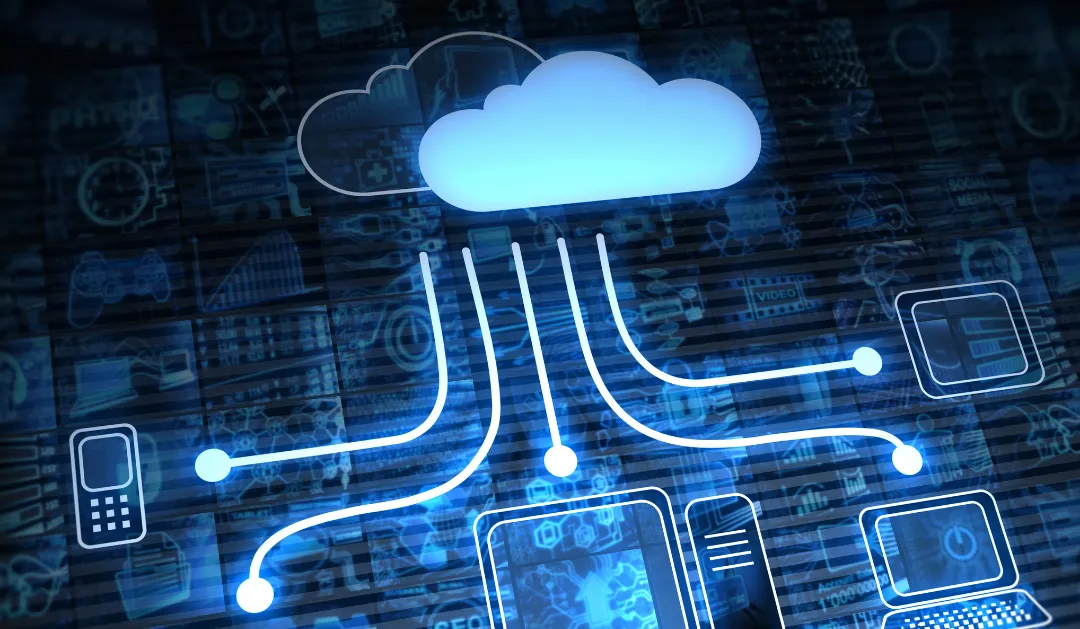

Due to increased competition, service providers must constantly improve their services in order to distinguish themselves from others. With the advent of server-less computing, developers just write code, and the cloud provider loads and executes that code in response to events. Server-less computing services include AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Azure Functions.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are two additional developing cloud technologies and services. These technologies offer a variety of cloud-based, ready-to-use AI and machine learning services to meet the demands of clients. The services include Amazon Machine Learning, Amazon Lex, Amazon Polly, Google Cloud Machine Learning Engine, and Google Cloud Speech API.